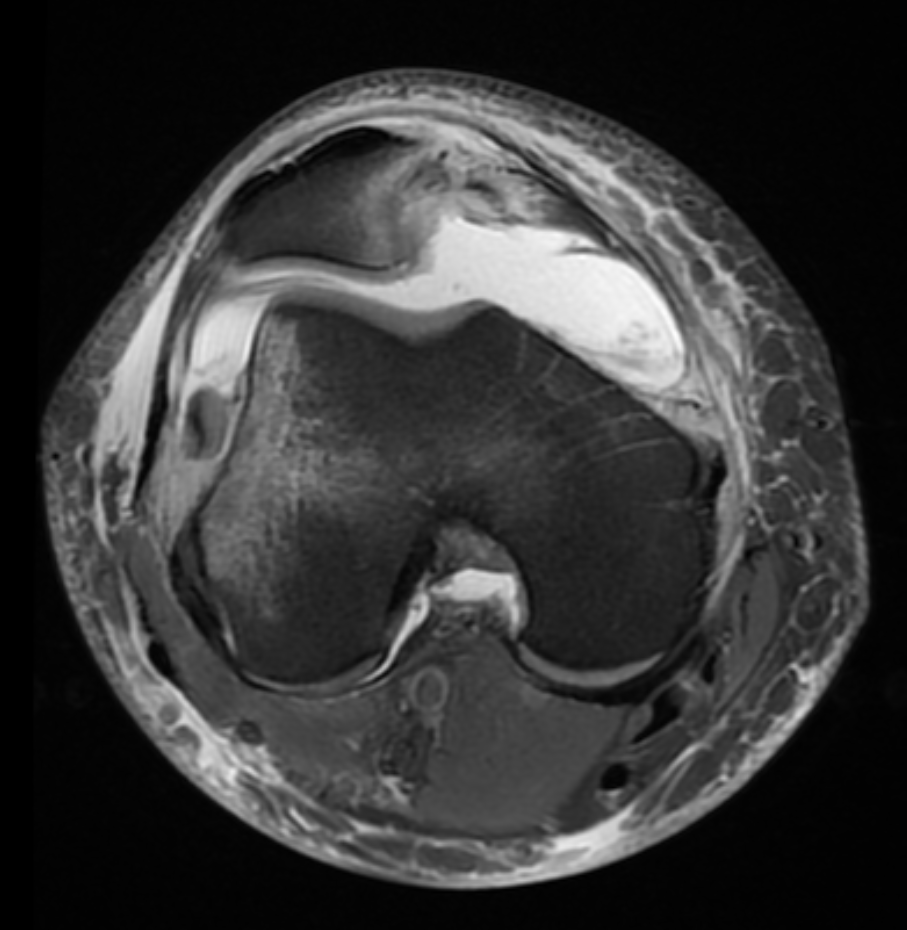
Typical constellation of signs
Report should note:
• Lateral condylar impaction microfracture
• Medial retropatellar microfracture
• Tear of MPFL
• Ant retropatellar cartilage shear injury
• Carefully look for inferolateral femoral condyle shear osteochondral fracture
ALSO
Patellar length
Patellar tendon length
TTTG
PTR= PTL/PL
Ratio of TTTG/PL also important
Tracking technique:
• knees are supported on a foam cushion in approximately 30° of flexion.
• Quadriceps loading is achieved by placing weights, using dedicated devices or decompressing an inflatable ball.
• a series of fast gradient echo sequences are obtained
• TR of 11 ms, a TE of 4.2 ms and a 15° flip angle.
• Seven 5 mm slices, six axial and one sagittal, are acquired in approx 8 s
• The axial slices are positioned to include the full proximal excursion of the patella as the knee extends. T
• This sequence is repeated 15 times giving a total imaging time of 2 min.
• Select the axial slice closest to the centre of the patella in each of the 15 sequences
• Compile these into a cine-loop
Various patterns of maltracking have been described.
A subjective grading is:
• 1, minor perceptible lateral deviation or tilt;
• 2, obvious lateral deviation or tilt; and
• 3, gross patellar subluxation.
As it subluxes, there is also a tendency for the patella to tilt laterally, presumably due to a rotatory force induced by quadriceps contraction