Common sporting associations with extensor carpi ulnaris tendinopathy include tennis hockey and golf
The tendon it lies in a sulcus on the posterolateral aspect of the ulnar head
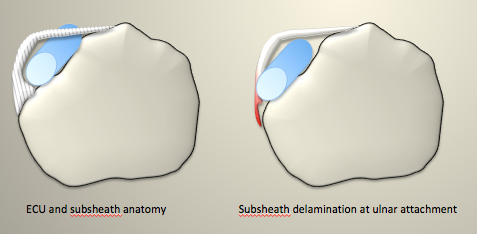
Immediately overlying the tendon is a sub sheath which is attached on the radial and ulnar sides of the tendon to the bony styloid.
The radial attachment is small, the ulnar attachment is more expanded and designed to resist tendon subluxation
Overlying these is the extensor retinaculum
Subluxation occurs as a result of ulnar quadrant failure.
Failure may occur either from disruption of the sub sheath itself or...
from a gradual delamination and separation of the ulnar attachment to bone.
Tenson subluxation may be apparent on static MR depending on the poition of the wrist during the examination
The diagnosis is more easily made by using dynamic ultrasound where,
on successive pronation and supernation the tendon can be seen to sublux.
Patients complain of pain on passive supination.
Tendonopathy and tenosynovitis are common, however
patients may also complain of pain with or without a clicking sensation due to subluxation of the tendon from its fibroosseous tunnel.
Tenosynovitis is also appreciated on MR or ultrasound images.
Increased fluid in the tendon sheath associated with signal or ultrasound changes within the tendon itself allow easy diagnosis of the stages of the disease.
PIFALL: The normal tendon often has a small central fibrous area which mimics focal tendinopathy
A prominent or previous injury to the ulnar styloid predisposes to extensor carpii ulnaris tendinopathy.
Rarely infective tenosynovitis may occur.
In these instances, the degree of synovial thickening on MR or ultrasound in association with marked enhancement of the tenosynovium or increased doppler signal are prominent.
Aspiration will yield purulent material though it should be appreciated that chronic calcific tendinopathy may mimic all of these findings
• Inserts into the pisiform
• Prone to calcific tendinopathy
• Friction of pisiform can occur as occupation hazard of mouse users
• Pisiform inserts via pisihamate and pisimetacarpal ligaments
• These can be injured in tennis