TIBIAL STRESS & SHIN SPLINTS
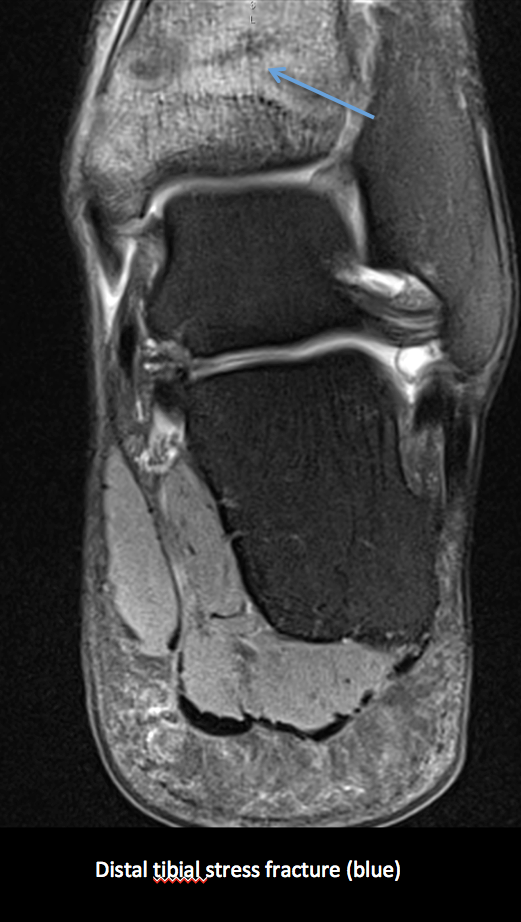
Active patients present with pain in the anterior tibia, most commonly distal third
Look for and report
• Soft tissue oedema
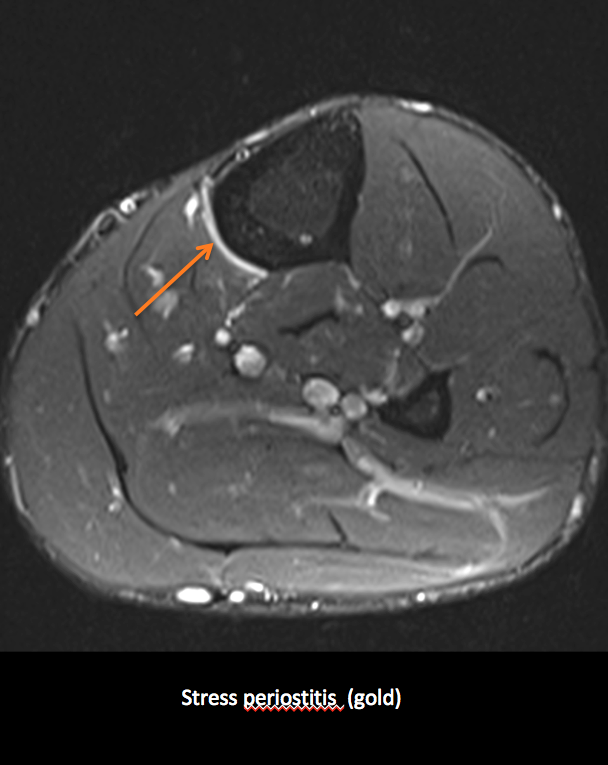
• Periosteal oedema and reaction
• Cortical involvement look specifically for fracture
• Medullary oedema
Soft tissue oedema along is sometimes included in the broad terminology of shin splints.
It is very non specific, oedema can result from vascular stasis or even local treatment with heat pads.
Linear cortical fracture with an area of thickened cortex can occur without soft tissue or marrow oedema
These lesions can be difficult to detect on MR
Look carefully at any areas of painful cortical thickening
Bergman AG, Fredericson M, Ho C, et al. Asymptomatic tibial stress reactions: MRI
detection and clinical follow-up in distance runners. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004;
183(3):635–8
Detmer DE. Chronic shin splints. Classification and management of medial tibial
stress syndrome. Sports Med 1986;3(6):436–46