• Medial elbow pain exacerbated by flexion against resistance.
• Pain is said to occur a little more proximal than UCL sprain.
• Trailing (dominant) arm most effected.
• Occurs in high-performance athletes requiring repetitive valgus and flexion forces
• Tennis, racquetball, baseball pitching, javelin, football, archery and swimming.
• Patients have point tenderness over the common flexor tendon, which is made worse by resisted wrist flexion.
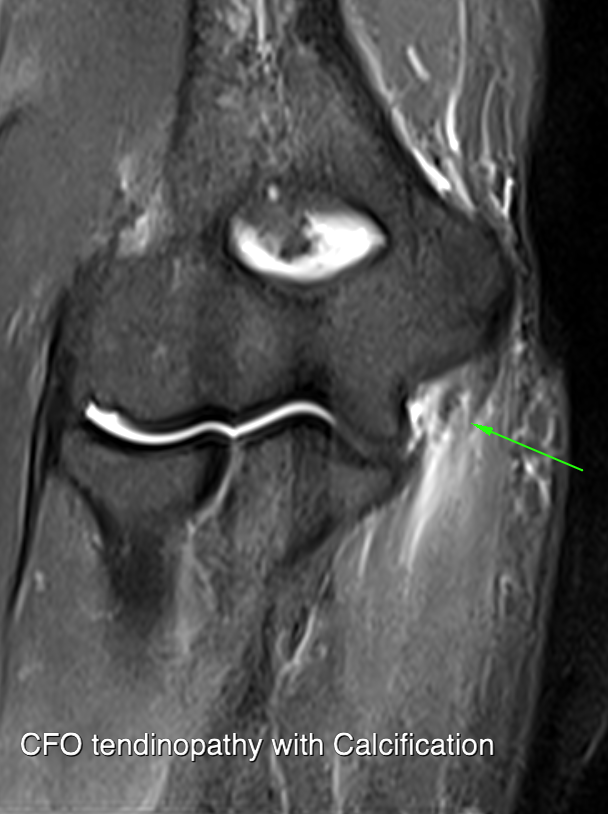
Coronal fat saturated proton density or STIR images are the mainstay for diagnosis.
High signal on WSS most common
Occasionall oedema in surrounding muscle when there is an acute injury
This is also called flexor pronator muscle sprain
principally involves flexor carpii radials and pronator trees.
as these are the principal tendinous components on the medial side.
Look for disorganisation of the tendinous common flexor origin with high signal
T1 weighted images also show signal heterogeneity replacing the normal low signal tendon, but care with magic angle phenomenon
Axial images provide supportive findings.